Cross-domain tracking on Google Analytics 4
Cross-domain tracking in UA is something you’re probably familiar with. Most configurations are done at the code level (e.g. In gtag.js or in GTM(GA tags). Many web analysts and marketers were confused by this confusion. Cross-domain tracking on Google Analytics 4 is much easier.
This guide will demonstrate how to set up cross-domain tracking in Google Analytics 4. We’ll first discuss the problem that cross-domain tracking solves, then we’ll move on to the actual configuration.
You don’t need an introduction? Jump to the configuration
If you’re already familiar with cross-domain tracking, then you can jump to this section. I’ll show you how to set it up in Google Analytics 4.
If you’re new to the subject, keep reading.
Multiple domains: The problem
This will make it very simple.
Google Analytics automatically tracks users using first-party cookies. When you land on a website, GA stores a “ga” cookie. Actually, GA stores more cookies but we will focus on the _ga that is stored in the visitor’s browser with some random identifier. Google Analytics monitors the cookie values as you navigate to pages A and B on your website.
GA knows that the cookie is still there (and the value is the same), so the second page view is included in the same session as the first page.
That’s awesome! You can use web analytics tools (not just GA) to track visitors’ usage of your website and what they are doing. Cookies, as technology have many drawbacks and are not perfect. Let’s just leave this topic for another blog.
Where is the problem?
Due to cross-domain policy, first-party cookies (created for your website) can’t be shared between different domains. Google Analytics on domainB.com won’t be able to recognize that a visitor is coming from domainA.com.
Google Analytics on domain A cannot reach certain cookies from domain A so it creates new cookies.
What is the result? Google Analytics (and other cookie-based web analytics tracking tools), will view you as two separate visitors on the domainA.com, and the domainB.com.
This is a huge problem. In your GA reports, will show too many users. Each person who visits domainA.com, as well as domainB.com, will become two users.
You can also track a new user and a session will start. In your traffic acquisition reports, you will see your domainA.com. This is known as “self-referral”.
![]()
What should you do? Track across domains.
What is cross-domain tracking with Google Analytics 4?
It is a workaround that allows webmasters/marketers/analysts to send user’s/visitor’s identifiers from domain A to domain B and preserve the session information. This allows the visitor to be tracked across multiple websites/domains.
Both websites must use the same GA4 property in order to make this work.
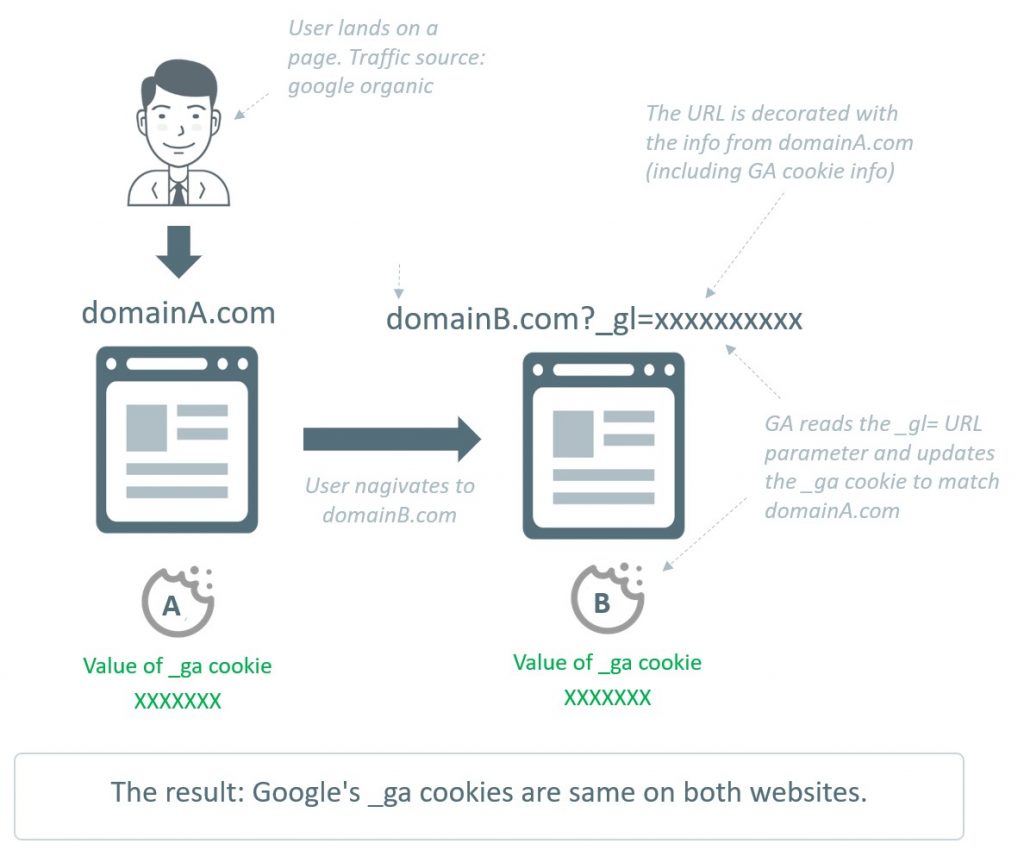
What is cross-domain tracking in Google Analytics 4?
This is the complete process.
Google Analytics 4 will send a special parameter to domainB.com when a visitor navigates between domainA.com and domainB.com. The GA on domainB.com can update Google Analytics 4 by using this parameter. It will also be able to understand that there is only one person who is navigating between two websites.
Google Analytics will track subdomains
Yes. You don’t need cross-domain tracking to do that.
You can track multiple websites belonging to the same domain, such as blog.yourwebsite.com. blog.yourwebsite.com and www.yourwebsite.com), Google Analytics 4 will handle that automatically.
If you search for “is subdomain considered cross-domain?” the result is NO.
How do you configure cross-domain tracking within Google Analytics 4
Okay, now that you have a better understanding of the problem and the solution, it is time to set it up.
Remember to follow one rule before you start: both websites (that are included in cross-domain tracking), must have the SAME GA4 property. You can either install the code directly on your site (tag), or via GTM. It is important to do this in the same property.
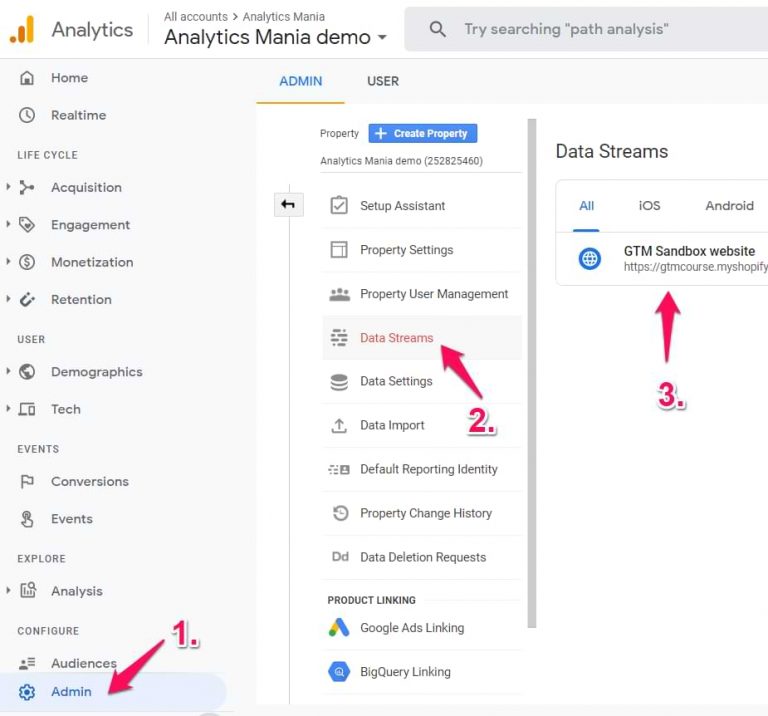
Step 1. Navigate to the Administration of Google Analytics > Data streams and choose a web data stream.
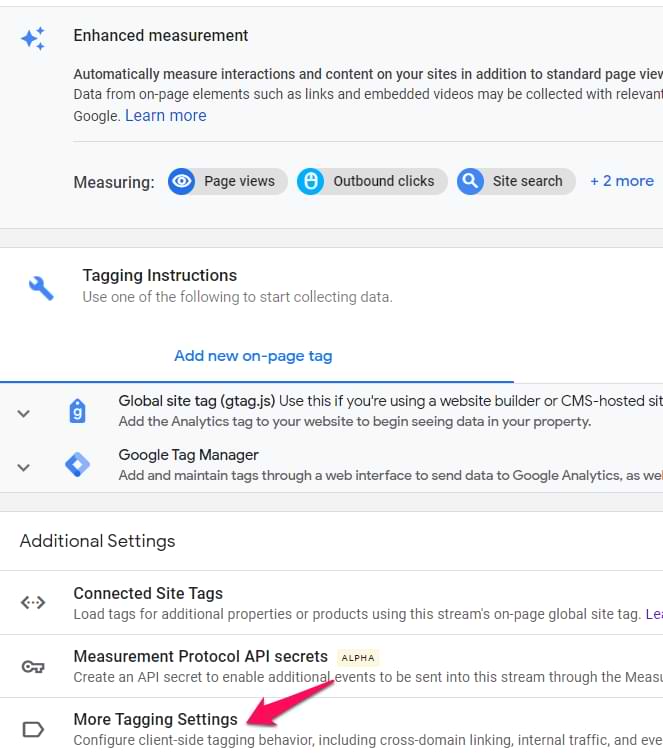
Step #2. Go to More Tagging Settings.
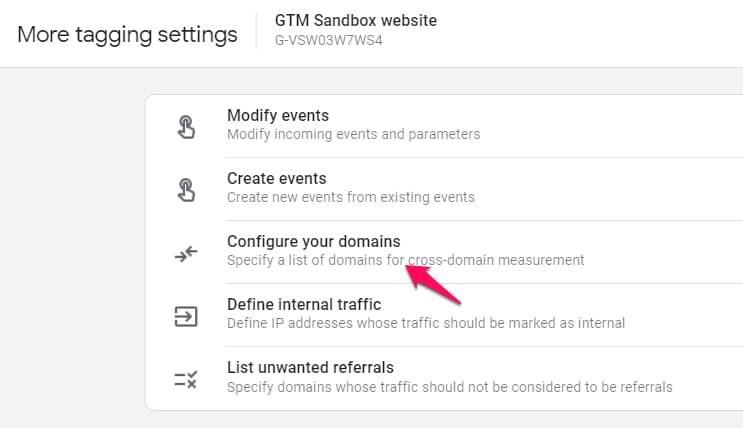
Step #3. Click Configure your domains.
Step 4. Enter all domains to be included in the cross-domain tracking setup. Save the file.
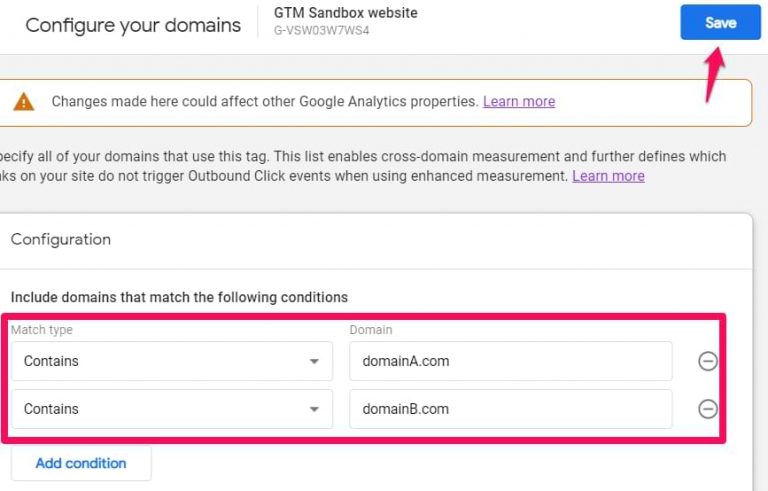
That’s all. This is all you need. GA will take care of that.
Note: If you run Universal Analytics on a website, you must remember something. Both GA versions share the _ga cookie. Your cross-domain configuration in Google Analytics 4 admin must match the settings for Universal Analytics. This means that the domains used in both configurations should match.
This will also impact your automatic outbound clicking tracking in enhanced Measurement. You will no longer be treated as an outbound click for domains you enter here.
Check the setup
After saving your changes, wait a while and then go to domainA.com. You will need to create a link on that website that redirects the visitor to domainB.com.
Click it. After you have been redirected to the second domain, verify the URL. You should include the _gl= parameter and a lot of other stuff.

You can then enable the GA Debugger extension, and go to the DebugView section of Google Analytics 4. Once you’ve done that, you can find your device in the a href=”https://www.analyticsmania.com/post/debugview-in-google-analytics-4/”>DebugView section of Google Analytics 4. In some cases, page_location parameter may contain the domainA.com. In other cases, it will contain domainB.com.
This is what you should be looking at.
Remember the redirects
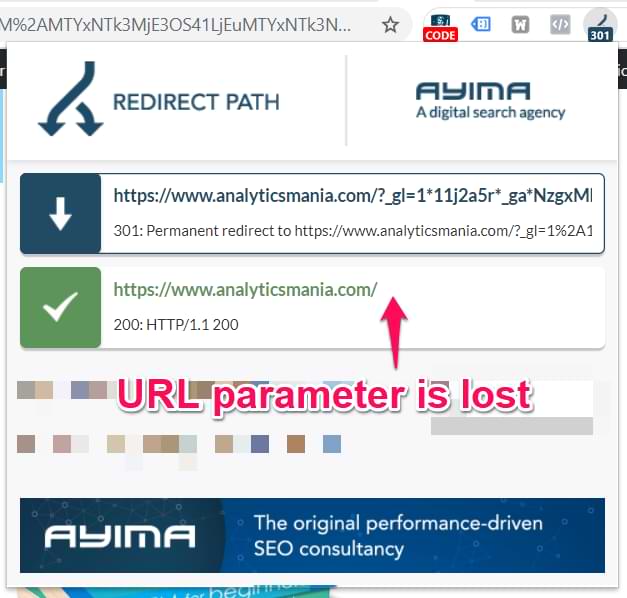
DomainB.com URLs that do not contain _gl parameters might have a JavaScript redirect. To identify issues, use the extension Redirect path.
After installing the plugin, go to domainA.com to click on the link to domainB.com. Click on the Extension Redirect Path to check if the parameter _gl was present. You should contact your developers to verify that it was there at first. This is where you want to keep the _gl parameter.
Questions frequently asked
Although some of these questions are already answered in the blog post, I will list them here because not everyone reads every sentence. Here’s the TL-DR version.
What is cross-domain tracking with Google Analytics 4?
It is a workaround that allows webmasters/marketers/analysts to send user’s/visitor’s identifiers from domain A to domain B and preserve the session information. This allows the visitor to be tracked across multiple websites/domains.
Why is cross-domain tracking important?
It is essential to ensure that your visitors are accurate and increase in number. The number of sessions will also increase as the visitor navigates to a second domain. A new session will be initiated (because GA considers this a different user).
Is cross-domain tracking necessary for subdomains
If you’re referring to subdomains of the domain, no. Google Analytics 4 (and earlier versions) can track visitors across subdomains. You don’t need any extra configuration.
What do I need to do to set up the referral exclusion for cross-domain tracking with Google Analytics 4
No. Google Analytics 4 automatically handles self-referrals based on domains you have entered in the section “Configure Your Domains” ( source). Referral exclusion lists are required for things such as payment gateway domains.
How can I test cross-domain tracking?
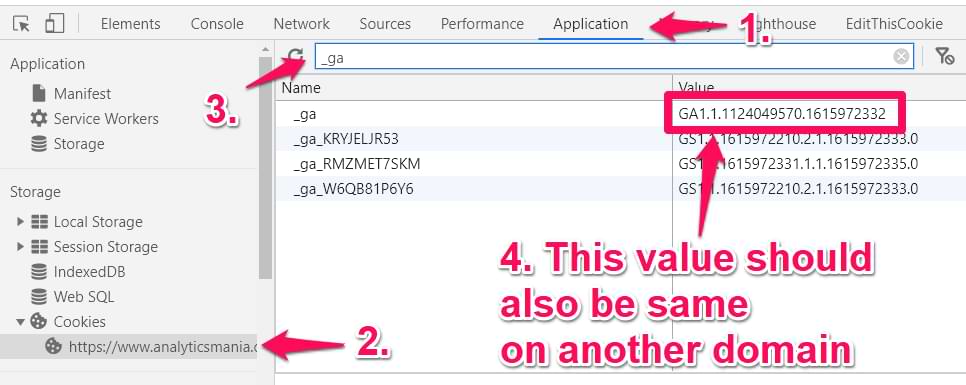
Click the link on the first site to verify cross-domain setup. It will redirect you to the second site. The URL of the second website must contain the _gl= parameter. You can also check the _ga cookie to confirm.
Check both domains using the screenshot below. Both domains must have the same _ga cookie value. Keep an eye on “Domain” in the cookie list.
Google Analytics 4 Cross Domain Tracking – Final words
Cross-domain tracking in GA4 is easier than Universal Analytics. There is no allowLinker nor Auto Link domains.
Go to the administrator of your GA4 property >Data streams and set up your domains in Web Stream.
Google Analytics 4 is clearly showing the direction Google is heading: less configuration in code or GTM and more in the GA4 interface. However, this does not mean that GTM is no longer necessary. Google Tag Manager is still necessary for many purposes.









