
How to do SEO audit for the website
Finding issues or mistakes that could keep your website from ranking on Google and other search engines is the process of doing an SEO audit. An SEO audit is composed of several components, including:
- ensuring that Google properly crawls, indexes, and displays your website;
- looking for on-page SEO issues on your website;
- checking your off-page SEO for any potential concerns on other websites that are related to or link to your site confirming the quality of the user experience on your website (for both mobile and desktop users);
- content optimization for keywords Checking your website for redundant or inadequate content;
- setting up and maintaining thorough reporting to monitor the operation of your website
Why Are SEO Audits Important?
With the use of SEO audits, your website and company can avoid:
- losing organic traffic as a result of bad site health;
- not taking advantage of sales possibilities or losing ground to rival brands;
- poorly indexing your website, which prevents searchers from finding it;
- being penalized by Google for harmful backlinks;
In summary, an audit of your website might identify issues that can be losing you visitors and sales.
The Tools You Need to Conduct an SEO Audit
The good news is that performing an SEO audit successfully doesn’t require a lot of SEO tools.
There are five major instruments we’ll use during the audit process:
- The website analysis tool, like Semrush, Seranking, Serpstat or similar that can provide you technical website audit.
- Google Analytics – Google Analytics offers metrics and information regarding the effectiveness of your website within their search engine.
- Google Search Console – Using Google Search Console, you can check to verify if your website is correctly indexed and how it is showing up in search engine results pages.
- Google PageSpeed Insights – PageSpeed Insights gauges how well your site performs on desktop and mobile platforms.
- Testing Google Schema Markup — You should ensure that the code is written accurately and without errors, if you’re creating schema for your website (which we’ll discuss in a moment). You are able to test and confirm that your schema is error-free using the Google Schema Markup Testing tool.
What is an SEO Audit?
Go ahead and use a site auditing tool to perform a site crawl before you begin the audit process. Any site audit tool that you feel comfortable with should work, though our free version of our program can help you get started.
Depending on the size of your site, it may take some time to finish because we will be using the insights from this report as we go through each phase.
First of all, launch your website auditing tool by choosing “audit website” and fill the website URL.
Make sure to verify your website in Google Search Console if you haven’t previously.
After covering the fundamentals, let’s talk about how to conduct a site audit.
SEO Audit Fundamentals: The Things You 100% Must Check
Let’s begin the audit with the items that you have to examine without fail.
Those potential problem areas that might keep your website from being properly crawled and indexed or major problems that might be the source of a problem.
1. Compare Your Rankings to Others and Research Your Rivals
Understanding the competition is necessary before delving deeply into a technical SEO audit or on-page review.
The more you are aware of what other companies in the same market are doing, the higher your chances of success will be, whether you are developing a new site for the first time or auditing as part of your ongoing plan.
You must profile your performance against the competition and benchmark the ranks of your website.
And the Semrush toolkit allows you to accomplish all of this.
Benchmarking the Rankings of Your Website
You need to set up position tracking for your website if you haven’t previously.
To start a new project, go to the Position Tracking tool.
Choosing your region, device, language, search engine, and filling out your full business name are the next steps in building out your campaign.
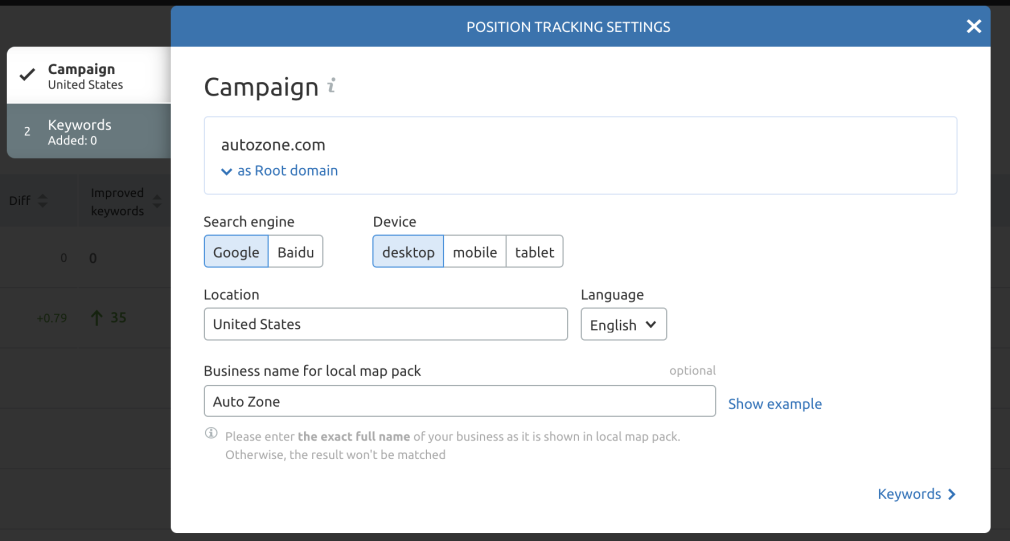
The next step is to enter your tracking keywords.
The addition of keywords can be done in a number of ways, including manually, through campaigns or Google Analytics.
Once the tracking process has begun, you can see your position for the given keywords.
Visit the Competitors Discovery report to see how your rivals are performing for the same keywords.
Recognizing Your Competition
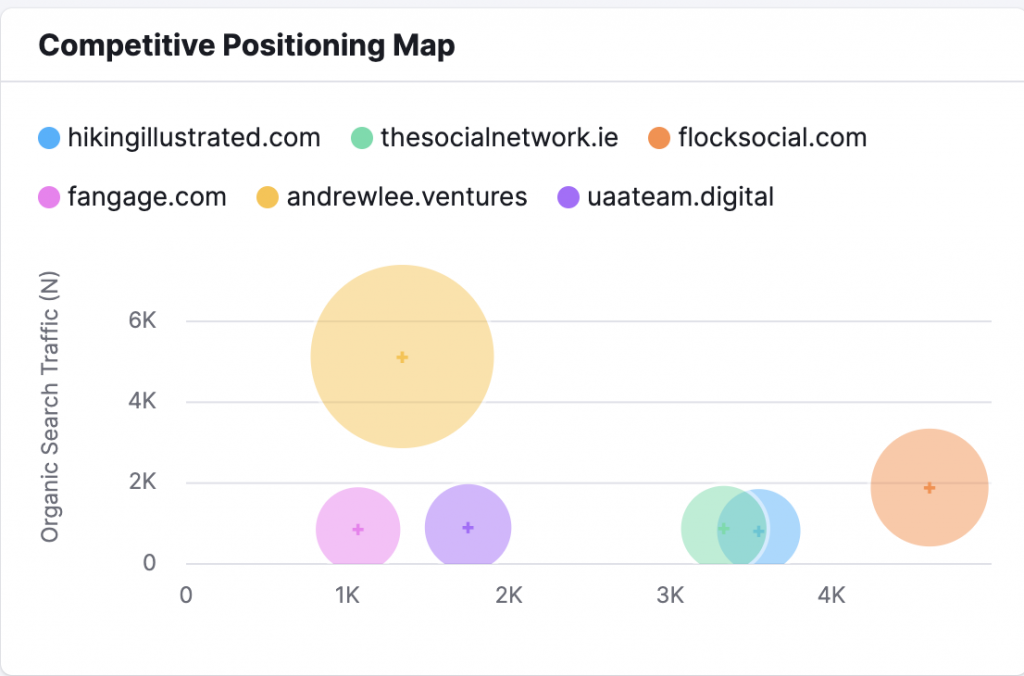
To get a broader view of your rivals, go to the Organic Research tool.
After entering your domain, select the “Competitors” option. A Competitive Positioning map will automatically populate, and a report on your top 100 rivals based on competition level will be displayed.
2. Verify whether Google’s index contains duplicate copies of your website.
Although it may be the simplest test you can perform on your website, it is crucial to make sure that Google is only indexing one version of it. Confused?
You could put your website on:
http://www.domain.com
http://domain.com
https://www.domain.com
https://domain.com
There isn’t much of a distinction here for the user (except that they may see a warning for a non-secure site in their browser).
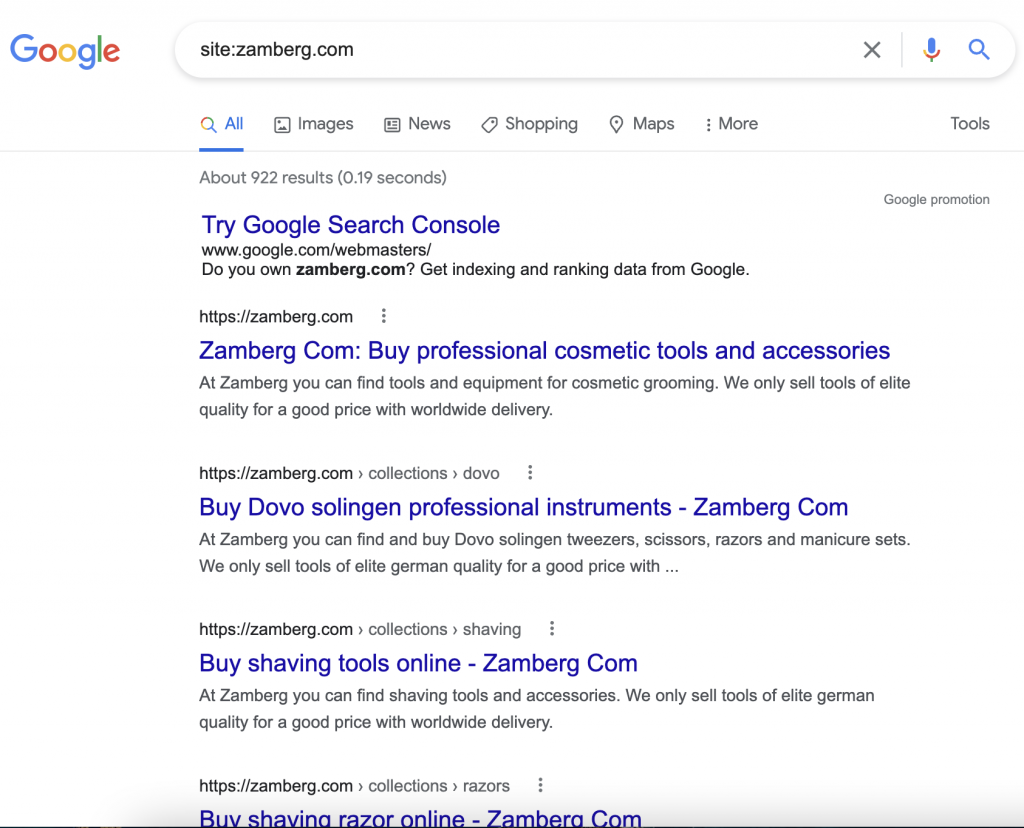
These represent various iterations of the website to a search engine. You must search for duplication and only index one version of your website. Fortunately, you can quickly verify this.
The indexed URLs for your domain are returned by this.
You may need to address a problem if you see multiple site versions.
The other option is to manually type each URL variation into your browser. Whichever you choose, you should anticipate being sent a single version. If not, use a 301 redirect to point to a single version.
Having stated that, performing a web search is crucial. Additionally, you will have a rapid understanding of any subdomains in use. It’s not unusual to see duplicate site versions on subdomains created for affiliates.
3. Verify the indexed URLs for your website.
Although you can do this check concurrently with the step above, it deserves its own section.
Look at the number of indexed URLs after performing a “site: search” on Google.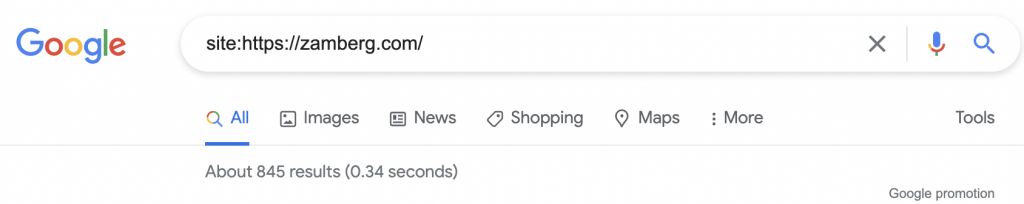
On occasion, you’ll be astounded by how many pages Google has indexed.
How many products are listed on your e-commerce site, if you have one? How many articles and pages have you produced in your CMS if your website only generates leads?
This is only a fast check to see if the number of indexed results matches your expectations.
If not, you can have a problem with thin or duplicate content pages that need to be fixed.
It’s important to note that you can use the Google Search Console Removal tool to de-index or otherwise prevent specific pages from showing up in search results. We will discuss this further in the auditing process. Please take note that these must be URLs that you control and have submitted to Google Search Console.
Examples include the rapid appearance of hundreds of thousands of indexed URLs in an e-commerce store with 5,000 products; this is typically due to faceted navigation that is indexable.
On the other side, if the outcome is lower than you anticipated, you can discover that your website isn’t properly being crawled or indexed. Below, we’ll go into more detail about this.
4. Examine any manual actions.
In the event that your website transgresses Google’s Webmaster Quality Guidelines, Google may take manual action against it.
Previously, this was known as a manual penalty. It implies that until Google reverses the decision, your site’s rankings will decline and you won’t be able to rank as highly as you did before. Either a page-level action or a site-wide action can be taken.
In the worst situation, your entire website will be deindexed and will not even rank for your brand name.
In Search Console, you may see if you’ve received a manual action. A “Security and Manual Actions” tab with a manual actions link can be found in the menu on the left-hand side.
When you click it, a page displaying the status will load.
Ideally, you can see a green tick indicating that there are no problems.
Additionally, we provide a useful handbook for navigating and avoiding manual penalties.
5. Examine the Speed of Your Site
Website speed has been significant for a while.
A specific Page Speed Update that Google released in 2018 made speed a mobile ranking factor.
When 2021 rolled around, Google released its Page Experience Update. Today, as many had anticipated, UX is more crucial to SEO success than ever before.
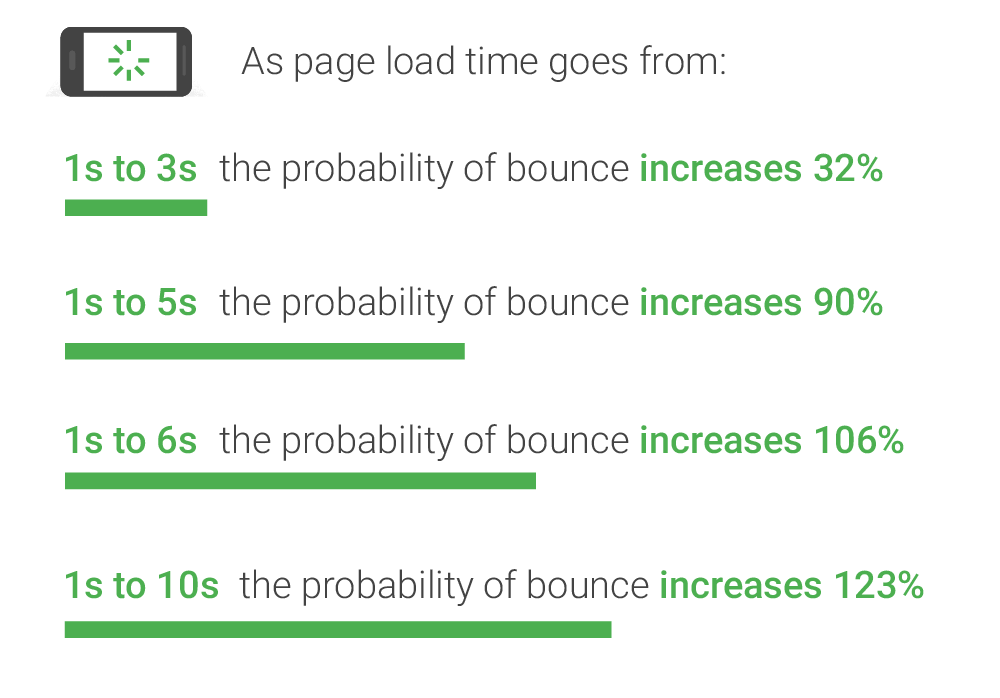
We cannot dispute the importance of speed.
According to statistics from Google that examine user habits, the likelihood that a user will leave a page quickly rises the slower it loads.
Your website’s speed is more crucial than ever, both from an SEO and user experience (UX) standpoint.
6. Verify Your Website Is HTTPS
It’s a good idea to upgrade to HTTPS if your website isn’t already set up that way. Previously known as “Socket Security Layer,” that “S” is now known as “Transport Layer Security.”
The HTTP protocol is simply an encrypted version of that “S,” to put it simply. For anyone viewing your website, it adds an additional degree of cyber security.
You can see your website’s score and a list of possible problems here. If this page only shows green checkmarks, take the time to fix any issues before continuing to the next step.
Remember that since 2014, HTTPS has been a ranking indication, thus if your site is still using HTTP, you must install an SSL certificate.
Let’s Encrypt makes this possible without cost.
7. Look for problems with mobile-friendliness
In today’s mobile-first environment, if your website isn’t mobile-friendly, it’s likely that you aren’t prioritizing the user experience.
Since 2015, mobile-friendliness has become a ranking element. The majority of websites are, in fact, either responsive or employ separate mobile-optimized versions, although this does not preclude the existence of problems.
And perhaps most significantly, starting in 2021, the Page Experience will be updated to include mobile-friendliness.
You may assess how well mobile versions of websites work using a helpful Google tool called the Mobile-Friendly Test.
The Mobile Usability area of the Enhancements page on the Search Console is another place to look for any problems.
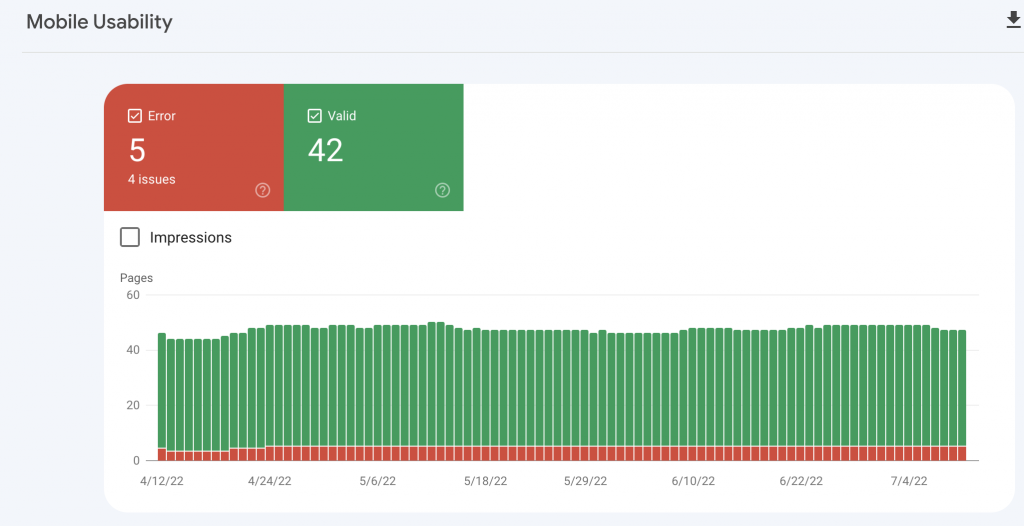
Here, any problems are mentioned. If not, you can mark that there are no problems.
To save loading time, the HTML on the pages has been reduced.
Search for “AMP Links” in the Crawled Pages report by navigating there. Any problems will surface on your website.
To see if your site has any AMPs at all, you can also access the Statistics report.
If a page has various versions (for example, an AMP version and a non-AMP version), you must set up a canonical tag to direct users to the preferred version.
Find out more advice on optimizing your website for mobile devices.
8. Examine and fix more indexation problems
Stay in Google Search Console and click the Index tab’s Coverage page.
Here, you can see pages that are valid or contain warnings, as well as discover coverage mistakes and excluded pages.
You must fix any problems that may be preventing your site from being properly scanned and indexed if you encounter errors in this area.
Typical mistakes include:
- Pages that are submitted in a sitemap but contain a noindex attribute
Pages in your robots.txt file that are prohibited from being crawled but are present in a sitemap include 404 pages.
You must fix mistakes if you find their source and know what caused them.
2. Disallowed URLs
A list of URLs that were excluded is also included in this report. These are web pages that Google is not currently indexing and may include:
pages with a noindex attribute omitted
website redirects
anomalous crawling
3. Issues with canonicalization
4. Crawled pages that are not indexed
5. 404 Not Found errors
6. Pages that your robots.txt file has blocked
These exclusions can occur for a variety of reasons and aren’t necessarily necessary to resolve.
For instance, it’s possible that you just moved to a different website. Redirects would be anticipated as a result of the move. Using noindex tags, you can also be preventing faceted navigation.
Analyze the report and address any issues that are raised. More information on how to achieve this may be found here.
9. Recognize the Page Experience on Your Site
Google’s Page Experience upgrade, which focuses on site performance and mobile-friendliness, has previously been mentioned above.
User experience is (finally) taken into account when rating websites.
Core Web Vitals was mentioned earlier, right?
Now is the time to incorporate this into your SEO audits. You should keep an eye on it frequently and respond to any problems that surface.
How About Core Web Vitals, though?
A project called Web Vitals was started by Google in May 2020 to offer standardized guidelines for quality signals that are crucial to achieving a great user experience.
Web Vitals are now considered a ranking element as of 2021. The good news is that you can now get a report within Search Console that will assist you audit these. The Core Web Vitals that you need to comprehend are:

This report can be found under the “enhancements” tab.
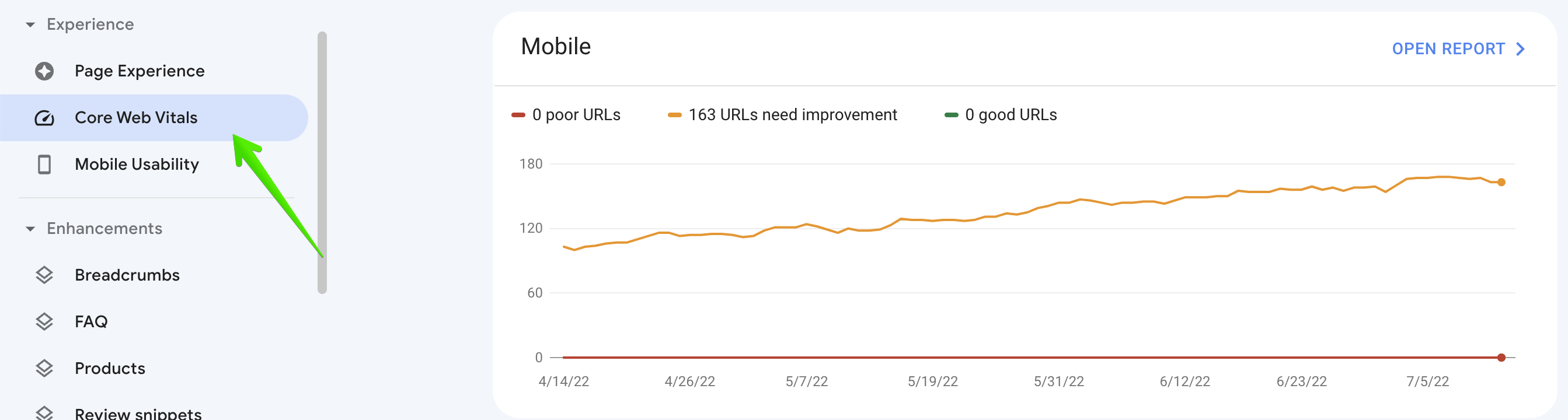
Opening one of these reports will provide thorough insights into the problems that exist in regard to bad URLs and those that need repair; take action as necessary. You will see a report that corresponds to both mobile and desktop.
10. Examine Your On-Page SEO On-page SEO involves issues like:
- the improvement of header tags, meta descriptions, and title tags;
- using appropriate image alt tags;
- making content that is optimized;
- creating a network of internal links;
- auditing on-page SEO components is essential because you have control over these optimization chances.
SEO Audit Fast Results
It takes time to run a successful SEO audit. It can be challenging to put forth so much effort only to see effects emerge gradually months after implementation.
The good news is that there are easy wins that can instantly enhance your website. These actions are a fantastic method to increase your self-assurance and achieve some quick successes. Let’s get going.
11. Correct faulty internal links
Internal links that are broken make for a bad user experience. When a visitor hits a link on your website, they anticipate being directed to that page, not given a 404 error. But even putting that aside, it gives search engines a bad quality signal.
Broken internal links are indicated in the Site Audit report’s Issues tab under the heading “Breaks.”
It’s as simple as updating the internal link to the proper URL or removing the link to fix issues.
You may also learn which pages pass the most “link juice” by visiting the Internal Linking Report to see which pages have the highest “Internal LinkRank.”
It may be wise to link to orphaned pages from more powerful pages with greater Internal LinkRank if it makes sense to do so.
12. Make Your Sitemap Cleaner
The main pages on your website are listed in the XML sitemap for Google to index.
You will find problems with improper URLs in your sitemap presented as faults in your Site Audit report.
These problems occur if your sitemap file contains URLs that point to pages with duplicate content, reroute to another page, or return status codes other than 200.
As a quick repair, give priority to eliminating any inaccurate pages from your sitemap.
13. Verify Any Redirects
It’s not unusual to encounter redirection-related problems, although these are frequently rather simple to identify and resolve.
The Site Audit report identifies a number of redirect problems.
Chains and Loops Redirect
Redirects can cause crawl problems if they aren’t configured properly. Chains and loops of redirects are frequent instances of incorrect redirect usage.
These will be indicated under the Issues tab.
Instead of 302 redirects, you should nearly always use 301 redirects. 301 redirects are permanent, as opposed to 302 redirects, which denote a more transient change. A 301 redirect is most likely the best option if you intend to retain items in their current location for the long run.
Look for any temporary redirects in the Site Audit report, and if any of them are meant to be permanent, upgrade them to 301 rather than 302.
Examining the Content on Your Website Content is king in SEO. Content keeps website visitors interested and learning. Therefore, it’s imperative to check that your material is comprehensive, practical, and performing well in search engines.
We will then explore how to remedy the problems that your audit uncovers and how you can conduct diagnostic work on your material.
14. Identify and fix issues with duplicate content
Duplicate content on your website can lead to problems that keep you from achieving the best possible rating. It can provide search engines conflicting messages.
After all, if there are two duplicate pages, which one should be ranked? Duplicate material can occasionally be seen as a ranking-manipulation attempt. This, however, is not as big of a problem as it formerly was.
Issues with duplicate material can be found in the Site Audit report’s Issues page.
15. Recognize pages with thin content
It’s still crucial to make sure your content provides adequate context and information for the subject you are writing about, even when it isn’t a direct ranking criterion.
Pages with little or no value for consumers and search engines are referred to as having thin content. Users that read this content are unlikely to convert and may possibly stop visiting your website.
For instance, if you are writing about a complex subject like “cataract lenses,” you should probably concentrate on the specifics of the lenses that are available on the market as well as the procedures that patients can use to obtain these kinds of medical solutions.
However, if you’re promoting a dog food company and want to emphasize the advantages of feeding your dog dry food, that subject might be more succinct and to the point. Most likely, this is not thin content.
Simply put, you’re providing the reader what they want in the exact number of words required to make your argument. In essence, this is a comparison of short- and long-form content.
Having said that, it’s crucial that you spot thin pages and fix these problems. There are two excellent choices:
Make these pages better by producing insightful, original content
If you want to stop the pages from being indexed, add a noindex property.
Usually, this will either make these pages better by producing excellent, original content or stop the pages from being indexed by adding a noindex feature.
Once more, these problems are indicated as pages with a low word count in the errors tab of your Site Audit.
16. Examine Searcher Intent and Compare Your Content to Top Ranking Pages
In recent years, searcher intent has been one of the most important factors that SEOs have concentrated on.
Spend some time examining the top-ranking pages for the search terms you’re aiming for, even though it may seem obvious. Consider conducting a content audit to rewrite your page with searcher intent in mind if you observe a significant disparity between your content and the pages that appear at the top of Google’s search results.
Maybe you haven’t delved into a subject enough? Users could anticipate reading a manual, yet you’re aiming to rank in the e-commerce category.
Fear not if you’re having trouble determining a keyword’s intent. In order to help you identify if a keyword is transactional (T), commercial (C), navigational (N), or informational, several of our keyword research tools now include a Search Intent Metric (I).
Conduct a backlink audit 18.
Links are still a significant ranking element. A backlink audit can be used to check for possibly harmful connections in addition to developing a plan to outlink your rivals.
Not all links boost your position. Links that Google deems to be an attempt to rig your search engine results are prohibited by their Webmaster Guidelines.
When conducting an SEO audit, it’s crucial to look for poisonous links, especially if this is your first time working on the site in question. We have a helpful tutorial that will walk you through poisonous backlinks if you’re not familiar with them or if you just want a reminder.
The Backlink Audit tool can help you find hazardous connections so you can remove them before they have a bad effect on the performance of your website.
There are a number of “toxic backlinks” that may be hazardous (you may filter for these in the tool’s “Audit” tab). In our tool, some detrimental elements that affect a backlink’s toxicity level include:
backlinks from unindexed websites
links coming from websites that have lots of mirror pages
links from link directories that point back
The tool also lists additional “possibly harmful” elements. This is especially helpful if you want to avoid any future backlink troubles.
Google prefers to accept “bad” backlinks as long as you didn’t pay for them or take part in another backlink scam, but if you notice a spike, it might be worthwhile investigating them.
Let’s now discuss how to start a backlink audit.
What Comes Next Following an SEO Audit?
Phew! You’ve completed your SEO audit, and you’ve identified a number of areas that require improvement. What follows is what? The job starts. Here are some items to check off your checklist after your audit is finished:
- Monitor your keyword positions and rankings (and keep tabs on competitor sites);
- To remove any duplicate content indexed by Google, use the Removal tool in the Google Search Console;
- Get rid of any clumsy programming that is impairing the performance of your page or making it difficult for Google to correctly render your website;
- Clean up your sitemap, fix any broken links, and change any 302 redirects to 301 redirects as needed (use the Schema Markup Testing tool to verify your code is error-free);
- Sort your links into the three primary categories, then start contacting publications and exporting your disavow list;
- Add at least one pertinent internal link to any orphan pages you find, and use the SEO Writing Assistant to help you create the most distinctive and original content on the internet;
- Start generating reports with our Reports function to check if the hard work you put into your SEO audit is paying off. This is especially crucial for organizations. Almost all aspects of SEO, including technical SEO, content SEO, and site audits, can be the subject of personalized reports for clients.







